

Similar exceptions to the 10% tax penalty apply when the beneficiary receives a tax-free scholarship, veterans’ educational assistance, employer-paid educational assistance and other tax-free educational assistance (other than gifts or inheritances). However, the 10% penalty is waived when the non-qualified distribution occurs as a result of the tax credit adjustment, up to the amount of the qualified expenses that justified the tax credit.
When the total 529 plan distribution is greater than the AQEE, the amount of the excess will be subject to income tax on the earnings portion of the withdrawal. If the student receives a $2,000 tax-free scholarship, the AQEE for the student in this example is reduced further, to $4,000. $10,000 – $4,000 (used to generate the AOTC) = $6,000 Adjusted Qualified Education Expenses (AQEE) If the beneficiary receives a tax-free scholarship, fellowship grant, Veteran’s educational assistance, employer-provided assistance or other tax-free educational assistance, the amount of the payment must also be subtracted from the total qualified expenses.įor example, parents who claim the AOTC and spend $10,000 on qualified higher education expenses in a given tax year may withdraw $6,000 from a 529 plan without tax consequences: To determine the amount of a qualified 529 plan distribution, any amount used to generate the federal education tax credit must be subtracted from the total qualified expenses.

If the student’s parent qualifies for the AOTC or LLTC, they must adjust their total qualified higher education expenses to avoid double-dipping. This includes 529 distributions used to pay for airfare and other travel costs, college application or testing fees, health insurance or room and board costs beyond the college’s cost of attendance (COA) allowance.
#Irs gov 529 qualified expenses how to#
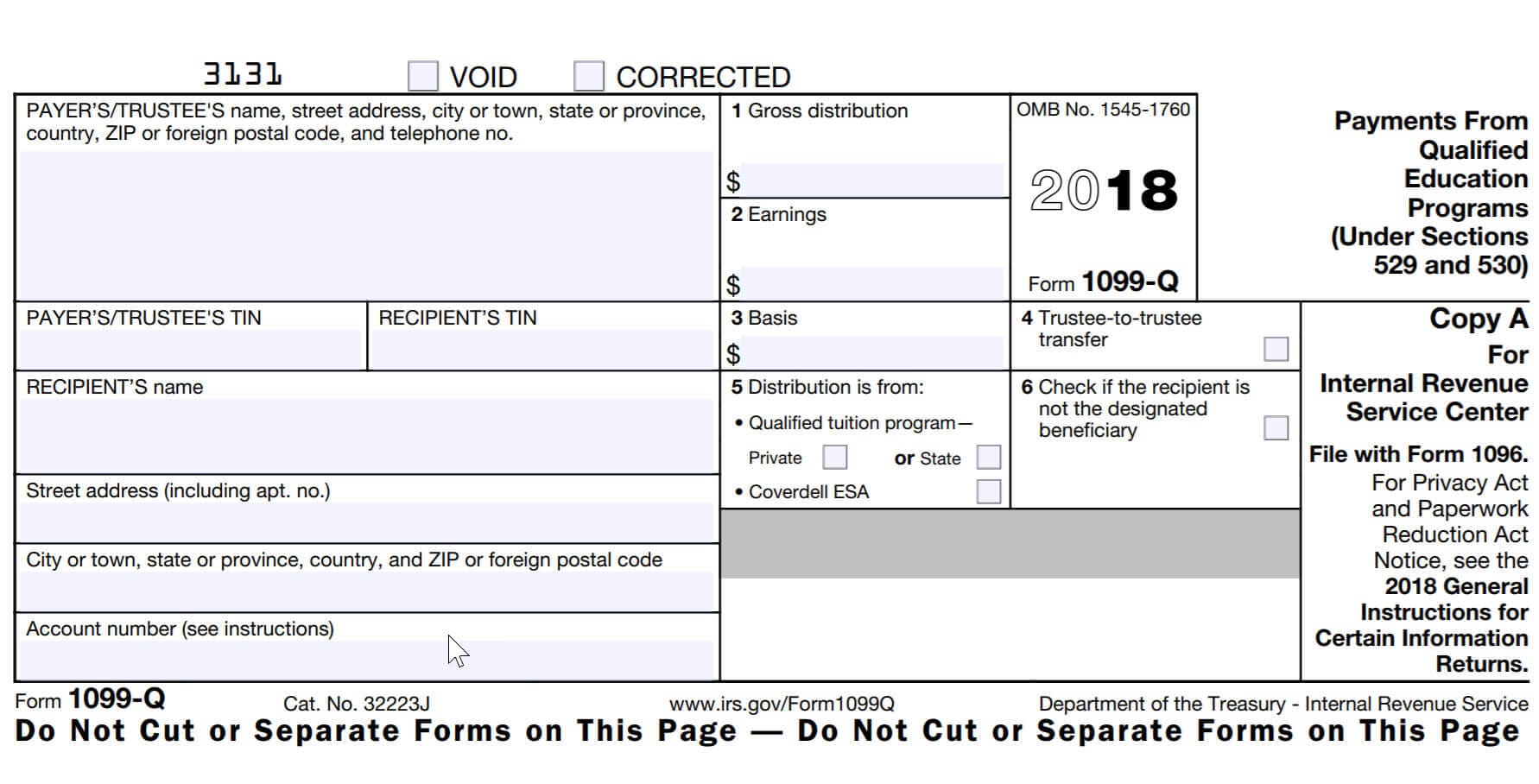
How to calculate 529 plan taxable distributionsĥ29 plan distributions used to pay for non-qualified expenses are subject to income tax and a 10% penalty on the earnings portion of the withdrawal. It’s up to the beneficiary and their parents to save receipts and calculate the total amount of qualified 529 plan expenses during the tax year. For example, Form 1098-T does not include room and board costs, computers and internet access, K-12 tuition, student loan repayments or costs of apprenticeship programs. Form 1098-T is used to determine whether or not the student qualifies for federal education tax credits, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) or the Lifetime Learning Tax Credit (LLTC).įorm 1098-T can be misleading because it does not provide a complete list of 529 plan qualified expenses. IRS Form 1098-T is a statement issued by a college or other eligible post-secondary education institution that lists the amount a student paid in tuition, fees required for enrollment or course materials required for enrollment. The earnings portion of a non-qualified 529 plan distribution is subject to income tax and a 10% penalty. Typically, Box 1 of a Form 1099-Q lists the total distribution, Box 2 includes the earnings portion of the distribution and Box 3 includes the basis, which is the contribution portion of the distribution. This typically results in a lower tax obligation than if the Form 1099-Q is issued to the parent or 529 plan account owner.įorm 1099-Q lists the total distributions from a 529 plan or Coverdell ESA during a given tax year, regardless of how the funds were spent. When the Form 1099-Q is issued to the 529 plan beneficiary, any taxable amount of the distribution will be reported on the beneficiary’s income tax return. The college, K-12 school or apprenticeship program the beneficiary attends.The Form 1099-Q will be issued to the beneficiary if the 529 distribution was paid to: IRS Form 1099-Q is a statement issued by a 529 plan or Coverdell ESA administrator that lists the amount of distributions in a given tax year. Form 1099-Q and Form 1098-T will list the amount of the 529 plan distribution and how much was used to pay for college tuition and fees, but it is up to the 529 plan account owner to calculate the taxable portion. When 529 plan funds are used to pay for qualified education expenses there is usually nothing to report on your federal income tax return.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
